Hey guys. Hope you all are surviving and enjoying the holiday season. In this week’s practice question, we’ll be covering test characteristics. Most of us are very familiar with tests, order sets, and determining which test(s) a patient needs. Today we’ll be going just a step deeper by covering characteristics of tests.
A healthcare test is a medical procedure that has a certain aim: detecting, monitoring and diagnosing diseases, as well as setting a course of treatment. Every healthcare test involves certain risks and benefits.
Possible risks of medical tests:
- Over-diagnosis
- Missed diagnosis
- Risks from the test itself
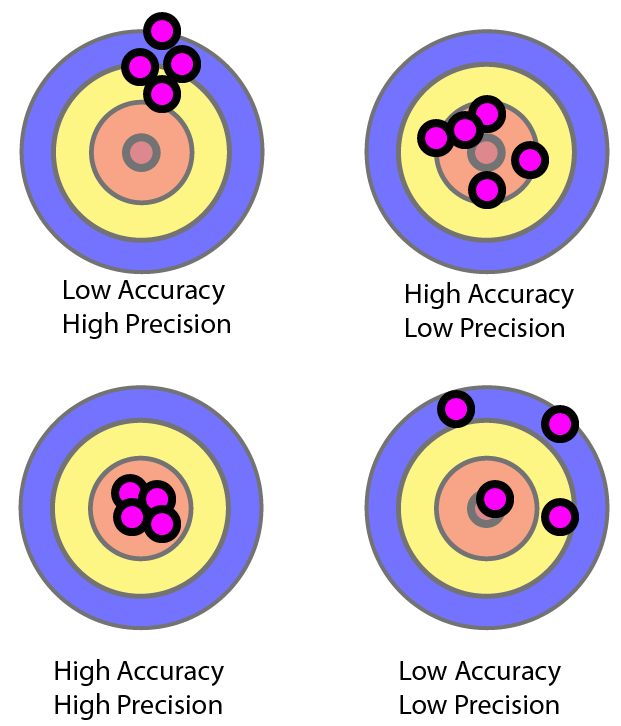
Accuracy of a healthcare test conducted in a laboratory is its correspondence with the true value. There are certain ways to maximize accuracy, for example by calibrating laboratory equipment with reference material.
Precision of a medical test can be achieved when repeated on the same sample multiple times. Test is considered imprecise if it has different results on repeated measurement.
There are positive and negative medical tests. If a test detects a symptom and sign of disease, a medical test is considered a positive test, while if a test doesn’t find a symptom or sign of disease, it is considered a negative test.
A quantification of a tested substance or entity is a common output of most blood tests and other tests. A quantification determines whether the tested entity is present or absent and in case it is the former, how much of it present.
The quantification in blood tests is well-determined, with specifications of mass concentrations, while other tests can be quantifications, too, but less determined compared to blood tests. At the same time, radiologic images are quantifications of radiologic opacity of tissues.
Most blood tests have results of continuous values, which means they can be analyzed in their output form, or they can also be converted to binary values by determining a cutoff value, when the healthcare result is considered as either positive or negative depending on the result value – if it’s higher than the cutoff, it’s a positive result; if it’s lower – it’s a negative result.
Interpretation of medical tests. When detecting a pathognomonic symptom or sign, it is most likely that the tested condition is present, while if the detection of the symptom or sign has failed, it is most likely that the tested condition is absent. But, in fact, the subjective probability of a test being positive or negative is never accurate to the extent of being either 100% or 0%.
Diagnostic medical tests usually use a reference group to have performance data on risks, likelihood ratios and predictive values.
Question
A low accuracy, high precision test would see which of the following characteristics?
A.) Results that are close to the true value and close to one another.
B.) Results that are close to the true value but not necessarily close to one another.
C.) Results that are not close to the true value but are close to one another.
D.) Results that are not close to the true value and not necessarily close to one another.
Answer and explanation
As you can see, a low accuracy, high precision test would have values clustered together, just not necessarily near the target value. Therefore, C is the correct answer in this case.
Recommended Reading and References
Error, Accuracy, and Precision
Kenneth E. Foote and Donald J. Huebner, University of Colorado
http://www.colorado.edu/geography/gcraft/notes/error/error_f.html