In this Explain it Like I’m 5 (ELI5) series, we’ll discuss network topologies. A topic you’ll need to understand for the clinical informatics board exam. For other posts like this one, be sure to check out other ELI5 posts like the ones listed at the bottom of this article.
Network topologies are how elements within a network are physically or logically arranged.
Physical topology describes how components like computers, cables, modems, and other network elements are physically arranged.
Logical topology describes how the data flows within the network regardless of its physical layout. Below are some of the common network topologies.
We’ll also discuss some of the nuances of each
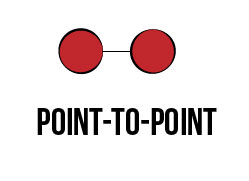
Point-to-Point
Point-to-point is the link between two endpoints. It is the simplest topology and can either be permanent or switched and traditionally does not involve data or packet formatting. A phone call would be an example of a point-to-point topology.
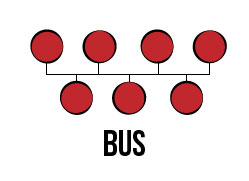
Bus
Bus topology connects nodes in a dasiy chain format using a linear sequence of buses. Buses are links that can transmit data in one direction. While this makes it easy to connect nodes such as computers and devices to a bus, if the connection is severed, the entire network shuts down. Because of this, bus topologies are best for small networks.
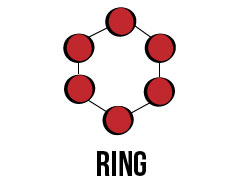
Ring
Ring topology transmits data around a ring until it reaches its destination. In a ring toplogy, every node acts as a repeater and every node is a critical link.
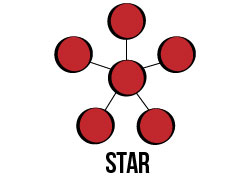
Star
Star toplogies connect each network host, computer, or peripheral to a central hub using a point-to-point connection. Because everything is pointed at the one central hub, if the hub goes down, then so does the network. However, star is advantageous due to the ease in which new devices may be added and the simplicity of its design and implementation.
Mesh
A network topology where each node relays data and cooperates in distributing data in the network. Nodes in a mesh network can be fully connected to one another (like the one displayed in the figure above), or partially connected to one another. Requiring physical connections between every node can become expensive and impractical for large networks. Therefore, mesh networks are usually wireless.
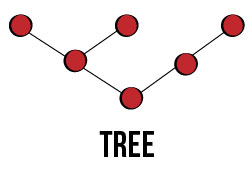
Tree
Tree toplogies use a heirarchal structure to connect nodes using point-to-point links. Secondary nodes can connect to a primary node and secondary nodes may have more nodes connected to themselves. Therefore, this toplogy can be scalable and easier to which node in a network is down. However, the higher level the node that goes down, the more nodes connected to the specific node that go down with it.
Hybrid
A hybrid topology combines two or more topologies. For example, a star ring network connects star topologies using a centralized hub while a star bus network combines star topologies using a bus trunk.
Daisy Chain
Daisy chaining refers to connecting network nodes in series with one another…typically in a linear or ring topology.